What volcanoes cause acidosis, what kinds of damage can volcanoes cause, what damages do volcanoes cause, what damage can volcanoes cause, what volcanoes are erupting now, what volcanoes are active, what volcanoes erupted this week, what volcanoes surround kilauea,
The formation of acid rain has been an enduring topic of interest for scientists and environmentalists alike. It is a phenomenon that has adverse effects on the environment and has been a major concern worldwide. The reasons for acid rain's formation lie in the components that make up the atmosphere. One significant cause of acid rain is volcanic gases that are released into the atmosphere.
Volcanic Gases Diagram
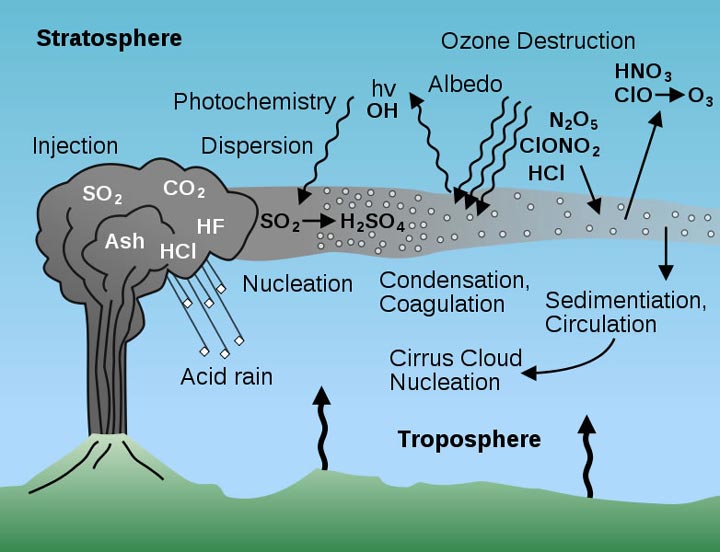
Volcanic eruptions result in the release of gases such as sulfur dioxide (SO2) and nitrogen oxide (NOx) into the atmosphere. These gases are primary pollutants that are responsible for the formation of acid rain. Volcanoes are a significant natural source of these pollutants and a considerable contributor to the total atmospheric emissions.
SO2 is a colorless gas with a sharp and pungent odor. It is highly reactive and soluble in water. When it reacts with water and oxygen in the atmosphere, it forms sulfuric acid (H2SO4). This reaction results in the formation of a cloudy and toxic mixture known as acid fog. NOx, on the other hand, is a group of gases that includes nitric oxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2). They are produced by high-temperature combustion, such as in vehicles and power plants. NOx reacts with atmospheric oxygen and water, forming nitric acid (HNO3).
How the Acid Rain is Formed?

Acid rain is formed when the sulfuric acid and nitric acid formed from the reaction of SO2 and NOx respectively with atmospheric elements dissolve in water droplets. These acidic water droplets can fall to the earth's surface in various forms, such as precipitation, fog, mist, and snow. The acid deposition has an adverse impact on the environment damaging the ecosystems, aquatic life, forests, and crops.
Acid rain also contributes to the erosion of buildings and monuments made of limestone, marble, and other materials that react with the acid. The acidic properties of rainwater accelerate the natural weathering process. Over time, this can lead to the loss of historical structures and sites.
The effects of acid rain can be seen globally, particularly in industrialized areas. However, the impact is more severe in areas with high levels of acid deposition. Lakes, rivers, and streams in these regions have become so acidic that aquatic life cannot survive, and entire ecosystems are destroyed. Soil's acidity in these areas also affects crops and vegetation, leading to devastating impacts on agriculture and forestry.
The control of acid rain emissions is a global issue, and many countries have taken steps to mitigate the problem. The implementation of clean air acts has led to significant reductions in sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide emissions. Countries have also developed technologies to reduce the number of pollutants and to recover sulfur from industrial processes.
In conclusion, the formation of acid rain is a severe environmental problem caused by the release of pollutants into the atmosphere. Volcanic gases, including sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxide, play a significant role in the formation of acid rain. The impacts of acid rain are severe, and it affects both the environment and human health. However, with concerted efforts to reduce acid rain emissions, we can mitigate its adverse impact on the environment and improve the overall wellbeing of our planet.
Also read:
.Blog Archive
Total Pageviews
Search This Blog
-
Soalan geografi tingkatan 1 arah angin, soalan geografi tingkatan 1 arah utara, soalan geografi tingkatan 1 awal tahun, kertas soalan geogra...
-
What volcanoes cause acidosis, what kinds of damage can volcanoes cause, what damages do volcanoes cause, what damage can volcanoes cause, w...
-
Contoh soalan sains komputer spm, laporan bengkel teknik menjawab soalan spm, soalan graf fungsi spm, soalan percubaan spm 2021 sains komput...

